E-retailers and other companies participating in the e-commerce supply chain are developing a variety of strategies for last-mile e-commerce distribution in urban areas. These strategies must account for a number of elements of local context which can be particularly challenging in emerging markets. Urban last-mile distribution strategies that are specifically tailored to these markets are rarely discussed in the literature.
In order to respond to the challenges of urban last-mile e-commerce fulfillment, companies must seek distribution models that perform well along multiple dimensions, such as cost-effectiveness, customer satisfaction, and sustainability. In this context, e-retailers and other companies participating in the e-commerce supply chain, such as parcel delivery companies, are developing a variety of strategies for last-mile e-commerce distribution in urban areas.
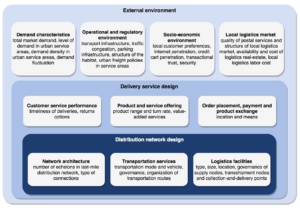
Current approaches differ according to numerous aspects, including the type and the location of logistics facilities, the type and size of the delivery vehicles employed, and the presence of alternative delivery and product exchange points. The specific design of last-mile e-commerce distribution strategies must account for a number of elements of local context such as local demand characteristics and customer preferences, regulations in place, or the operational characteristics of the environment in which they operate.
A study by Janjevic and Winkenbach of Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Center for Transportation & Logistics (CTL), uses a combination of literature review and case study analysis to establish an integrated conceptual framework that allows characterizing urban last-mile e-commerce distribution strategies in both mature and emerging markets. They then use this structured framework to perform a review and comparison of different last-mile distribution strategies and highlight variables impacting the choice of network design decisions. The paper presents different global examples of last-mile networks, like Konga, Alibaba, Flipkart, and Souq.